Testosterone, Peptides & Performance: What Men Over 40 Need to Know Before Jumping In
Introduction: Why Men Over 40 Are Searching for Performance Solutions
A middle-aged athlete stretching, representing active men over 40 who seek to maintain performance. Men in their 40s and beyond often start noticing changes in their bodies that affect performance, recovery, and libido. It’s not just in their head—male hormone levels, especially testosterone, naturally decline with age (about 1% per year after 40 on average ). This can lead to frustrating symptoms like fatigue, slower recovery from workouts, reduced muscle mass, increased body fat, lower sex drive, and mood changes . Unsurprisingly, many active men begin searching for ways to support testosterone after 40 and maintain their edge.
In this quest for vitality, two options frequently come up: Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) and peptide therapy. Both are touted for boosting performance and well-being, but they work very differently. What’s the difference between TRT vs. peptides, and which (if either) is right for you? In this article, we’ll break down how testosterone and peptides each play a role in men’s health, compare their benefits and risks, and provide guidance for men over 40 considering these interventions. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of each approach – and why education and medical guidance are so important before jumping in.
The Role of Testosterone in Men’s Health
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, and it’s central to many aspects of a man’s health and performance. In early adulthood, testosterone peaks, supporting the classic markers of vitality. As men age, levels gradually decline, which can impact various bodily functions. Here’s what testosterone does for men’s health :
• Muscle Strength and Mass: Testosterone helps maintain muscle size and promotes strength.
• Bone Density: It keeps bones strong and reduces fracture risk.
• Fat Distribution: It influences where the body stores fat (lower T can mean more fat, especially around the belly).
• Red Blood Cell Production: Testosterone supports red blood cell formation, affecting endurance and energy.
• Libido and Sexual Function: It fuels sex drive and is crucial for normal erectile function and sperm production.
• Mood and Energy: Healthy testosterone levels contribute to confidence, motivation, and overall vitality.
In short, testosterone is a key driver of the qualities that keep men feeling strong, virile, and energetic. By age 40, however, it’s common for men to experience a slow dip in testosterone each year . Not every man will have noticeable symptoms from this age-related decline , but many do start to feel the difference. Lower testosterone (sometimes called “low T”) can manifest as reduced gym performance, longer recovery times after exercise, diminished libido, and even difficulty concentrating or a drop in motivation.
Because testosterone is so critical, it makes sense that boosting low levels can have benefits. This is where testosterone support after 40 becomes a hot topic. Some men pursue natural strategies (more on that later), while others explore medical options like TRT to restore youthful hormone levels. Before deciding on any approach, it’s important to understand what each therapy entails and how it might affect your health.
What is TRT? Pros, Cons, and Medical Considerations
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) refers to medically supervised treatment that increases testosterone levels in men who are deficient. Essentially, TRT means introducing bio-identical testosterone into the body to raise your hormone levels back to a normal range. This can be done through injections (the most common method), transdermal patches, gels, or other delivery systems. In all cases, you’re adding external testosterone rather than relying on your body to produce more. According to medical experts, TRT involves providing exogenous testosterone to restore levels and alleviate symptoms of low T . It’s a standard therapy for men diagnosed with hypogonadism (clinically low testosterone) and is typically prescribed by a doctor after blood tests confirm the deficiency.
How TRT Helps: For men who truly have low testosterone, TRT can be a game-changer. By restoring this vital hormone, TRT directly addresses many of the issues caused by low T. Men often report benefits such as:
• Revitalised Energy and Mood: Many patients on TRT feel a renewed “zest” for life. Normalising testosterone can improve mood, motivation, and energy levels . Tasks that felt draining may become easier with balanced hormones.
• Improved Libido and Sexual Function: One of the most celebrated effects of TRT is the return of a healthy sex drive and better erectile function. Low T is notorious for sapping libido. Restoring testosterone can “reignite that youthful spark” in sexual desire and performance , greatly improving intimacy and confidence.
• Increased Muscle Mass and Strength: Testosterone is anabolic, meaning it helps build muscle. Men on TRT often find it easier to gain lean muscle and recover from workouts. Muscle tone (especially in areas that tend to shrink with age, like arms and chest) improves when testosterone is back to optimum levels .
• Reduced Body Fat: Alongside muscle gains, TRT can aid in fat loss. Men with restored T frequently notice that stubborn fat (like belly fat) becomes easier to lose . Testosterone influences metabolism and body composition, shifting the balance toward more muscle and less fat.
• Sharper Mental Focus: Some men report cognitive benefits – better focus, memory, and mental clarity – once low T is treated . It’s as if a mental fog is lifted, improving productivity and concentration day to day.
These improvements can significantly enhance quality of life for a man in his 40s, 50s, or beyond who has been struggling with low-T symptoms. In fact, for the right candidate, testosterone replacement therapy can be life-changing . It essentially “restores a missing hormone” and brings your body chemistry closer to what it was in younger years.
Risks and Cons of TRT: While TRT offers many potential benefits, it’s not a decision to take lightly. There are important medical considerations and possible drawbacks:
• Hormone Suppression and Fertility: When you supply testosterone from outside, your body may reduce or even shut down its own testosterone production (through a feedback loop). This can lead to testicular shrinkage and significantly lowered sperm production, affecting fertility . Men who still plan to have children must weigh this and often need concurrent treatments (like hCG or other medications) to maintain fertility.
• Skin and Hair Effects: Increased testosterone can cause acne or oily skin in some men . It may also accelerate male-pattern baldness if you’re genetically predisposed (due to testosterone’s conversion to DHT, a hair-loss related hormone).
• Prostate and Hormone Balance: TRT can stimulate the prostate gland. Men with a history of prostate issues need careful monitoring, as testosterone might enlarge an existing benign prostate condition or, in theory, aggravate prostate cancer if it’s already present . Regular PSA tests and check-ups are a must on TRT. Also, some testosterone can convert to estrogen in the body, potentially causing gynecomastia (breast tissue enlargement) in certain individuals.
• Blood Thickness and Heart Health: One side effect of TRT is an increase in red blood cell production. Too many red blood cells (a condition called polycythemia) can thicken the blood and raise the risk of blood clots . Clots can lead to serious issues like pulmonary embolisms. Additionally, there’s been debate about TRT’s cardiovascular risks. Some studies suggested a link to heart issues, though more recent research indicates no major cardiac risk over a two-year period for men on TRT under medical supervision . In any case, a knowledgeable physician’s monitoring is essential to manage any risk factors (blood counts, blood pressure, cholesterol, etc.).
• Mood and Other Side Effects: Hormones can affect mood. Some men experience irritability or mood swings on TRT, especially if dosing isn’t well managed. Sleep apnea can potentially worsen with testosterone therapy as well. This underscores the need for individualised dosing and follow-up.
• Commitment and Maintenance: TRT isn’t a one-time cure; it’s an ongoing therapy. In most cases, once you start, you’re committing to regular treatments (injections weekly or bi-weekly, or daily gel applications, etc.) and routine blood tests. Stopping TRT abruptly will likely bring testosterone back down to previous low levels (or even lower, temporarily, due to suppression of natural production). So, you need to be ready for the long haul and a consistent routine.
Medical Oversight: Any man considering TRT should do so under the care of a qualified healthcare provider. In fact, you cannot legally obtain real TRT without a prescription – testosterone is a controlled substance, and doctors will typically require at least two blood tests confirming low levels before prescribing . This process is in place for your safety, ensuring that testosterone is truly needed and used responsibly. A doctor will also check for underlying causes of low T (like pituitary issues or medications) and might suggest treating those first. If age-related low testosterone is confirmed, a discussion of TRT’s risks and benefits follows. Generally, guidelines do not recommend TRT for men who have borderline or age-normal levels without symptoms – in such cases, lifestyle changes might be advised instead.
To summarise TRT: it’s a direct method of boosting testosterone – very effective for those who need it – but it comes with significant responsibilities. The pros (more muscle, mojo, and motivation) have to be balanced against the cons (side effects and lifelong commitment). Now, what about peptides, the alternative therapy that some hail as a gentler route?
What Are Peptides? Types and Their Effects on Performance and Recovery
Peptide therapy is an emerging area in men’s health and anti-aging circles. Unlike TRT, which introduces a primary hormone, peptide therapy uses short chains of amino acids (peptides) that act as signalling molecules in the body. These peptides can trigger your body to produce more of its own hormones or to initiate healing processes. In simpler terms, peptides often aim to stimulate natural functions rather than replace hormones outright . For example, certain peptides can prompt the pituitary gland to release more growth hormone, indirectly benefiting muscle growth and recovery, instead of directly injecting growth hormone or testosterone.
There are many different peptides, each with specific targets and effects. Here are some of the best peptides for men’s health commonly discussed, and how they relate to performance and recovery:
• Growth Hormone Releasers (GHRHs and GHRPs): Peptides like Sermorelin, Ipamorelin, and CJC-1295 fall in this category. They stimulate the release of Human Growth Hormone (HGH) from the pituitary. More HGH can lead to higher IGF-1 levels, which support muscle development, fat loss, and tissue repair. These peptides aim to mimic the body’s natural growth hormone pulses, thereby improving recovery, lean mass, and even sleep quality (since growth hormone is important for restorative sleep). For instance, studies have shown an HGH-secretagogue (MK-677, a oral compound) could boost growth hormone and IGF levels in older adults to youthful ranges – GHRP peptides are expected to have similar benefits by naturally nudging your own hormone production.
• Repair and Recovery Peptides: BPC-157 and TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) are popular for injury healing and reducing inflammation. Nicknamed the “Wolverine peptide” by athletes, BPC-157 has shown promise in accelerating tendon and muscle repair (in one study it sped up healing of rat tendon injury) . These peptides are not about building muscle directly, but rather about helping your body recover faster from the damage that comes with training or aging. Faster recovery means you can train harder and bounce back quicker. TB-500 is similarly used to promote healing and tissue regeneration. Some men over 40 use these after injuries or to alleviate joint pain and aches from years of wear and tear.
• Peptides for Libido and Wellness: PT-141 (Bremelanotide) is a peptide developed to address sexual dysfunction; it works on the brain to increase arousal. Unlike testosterone (which affects sex drive via hormones), PT-141 can directly boost libido and has been dubbed the “libido peptide.” It’s an example of how peptides can target specific issues – in this case helping men (and women) with low sexual desire . Other wellness peptides include ones like Semax or Selank (for cognitive function and anxiety reduction), and Thymosin Alpha-1 (for immune support), indicating the wide range of possible applications.
Each peptide has a unique function, and researchers are exploring their use for everything from muscle growth to fat loss, immune function, and skin health. Enthusiasts claim that peptides offer a more “targeted approach” with potentially fewer systemic side effects: “They’re mimicking what your body already does but with more specificity – it’s the difference between using a hammer and a scalpel,” as one doctor explained .
Potential Benefits of Peptide Therapy: Early research and anecdotal reports suggest peptide therapy can yield a broad array of benefits for middle-aged men seeking performance and recovery boosts. Some of the touted benefits include:
• Enhanced Muscle Recovery and Growth: By elevating growth factors and improving tissue repair, peptides can help you recover faster from workouts and potentially increase muscle mass over time . For example, in addition to healing properties, growth hormone-releasing peptides support protein synthesis and muscle building. This means less downtime and more progress in the gym.
• Improved Fat Loss and Metabolism: Certain peptides may aid in reducing body fat. HGH-releasing peptides, in particular, often lead to improved metabolism and utilization of fat for energy . Men have reported a easier time shedding abdominal fat when using these therapies alongside diet and exercise.
• Joint and Injury Healing: As mentioned, BPC-157 and TB-500 are known for their healing potential. These can be beneficial for men over 40 who have nagging injuries or joint pain. Faster healing and reduced inflammation mean you can stay active with less discomfort.
• Increased Vitality, Sleep, and Well-being: Some peptides can improve aspects of well-being like energy levels, sleep quality, and even skin appearance. By stimulating processes like collagen production and cellular regeneration, peptide therapy has been noted to make users feel and look more youthful . For instance, patients on certain peptide regimens have reported feeling “10 or even 20 years younger” in terms of vigor and resilience (though individual results vary).
• Milder Side Effect Profile (Generally): Because most peptides work within your body’s natural systems, they tend to have milder side effects compared to introducing a powerful hormone like testosterone or synthetic HGH . Your body recognizes them as signaling molecules, and if it doesn’t need the extra effect, often the peptide is simply broken down. Common minor side effects can include temporary injection-site irritation or headaches, but serious effects are rare when peptides are used properly .
Risks and Considerations with Peptides: It’s important to temper the enthusiasm with some caution. Peptide therapy is still relatively new in practice, and there are several considerations:
• Variable Regulation and Quality: Unlike testosterone (which is a well-defined medication), many peptides exist in a gray area of regulation. A few are FDA-approved for specific medical conditions, but most anti-aging or performance uses are off-label . This means you must be careful to get peptides through legitimate medical providers or compounding pharmacies. There have been issues in the past with online “research chemical” peptides that might be impure or inaccurately dosed. Always working with a knowledgeable physician is key to ensure you’re using high-quality, properly sourced peptides .
• Lack of Long-Term Research: Perhaps the biggest unknown is the long-term safety of many of these peptides. While early studies are promising, we don’t yet have large-scale, long-term clinical trials for most peptide therapies . We know testosterone’s effects (good and bad) from decades of research; peptides, not so much. As one health publication noted, the “kind of large-scale clinical trials you depend on to know whether something’s worth it? Not there yet” for most peptides . So, one should approach peptide therapy with an informed but cautious mindset – we’re still learning about efficacy and side effects over the long haul.
• Side Effects and Unknowns: Although generally mild, peptides are not completely side-effect free. You may experience small issues like injection pain, water retention, or headaches depending on the peptide. More significantly, because peptides can affect hormone balances (like raising HGH or IGF-1), there could be unforeseen impacts (for example, excessive IGF-1 has been linked in some contexts to cancer risk, though this is not fully understood). “Milder” doesn’t mean zero risk . It’s also possible to over-stimulate a hormone system (e.g., taking too high a dose of a growth hormone-releasing peptide could strain your pituitary). Thus, medical guidance is still crucial.
• Administration and Cost: Most peptide therapies involve subcutaneous injections (a tiny needle under the skin) daily or a few times a week. Some people are fine with this, others might find it inconvenient compared to TRT injections that might be only weekly. There are a few oral or nasal spray peptides, but injections are most common because peptides can be broken down in the digestive system. Cost-wise, peptides can be expensive, but often they’re cheaper than illicit growth hormone; still, using multiple peptides or long-term therapy can add up. Insurance generally doesn’t cover peptide therapy (since it’s off-label for wellness purposes), whereas TRT might be covered if you have a documented deficiency.
• Are Peptides Safer than TRT? This is a frequent question. The answer is complex. In terms of specific side effects (like prostate issues or polycythemia), peptides don’t cause those directly the way testosterone might. In fact, peptides are often marketed as a “safer way to get gains without the side effects of riskier options like testosterone or synthetic growth hormone” . It’s true that peptides typically don’t come with things like hair loss or major cardiovascular strain, and users generally tolerate them well . However, “safer” doesn’t mean “foolproof.” The relative safety might be higher in some ways, but remember the lack of long-term data. Testosterone, at least, is predictable when monitored; peptides are still being researched. Also, if a man actually has clinical low testosterone, peptides (unless it’s a specific one to increase testosterone indirectly) won’t fix that – TRT would be needed. So, it’s not that one is universally safer than the other; it depends on the context and how they’re used. Both therapies should be overseen by a medical professional to ensure safety.
In summary, peptide therapy offers a fascinating and potentially effective avenue for men over 40 to improve their performance and recovery. It takes a more nuanced approach – using the body’s own chemistry – and for many men, that’s appealing. You might see peptides as a way to get some benefits of hormone optimisation without “going on steroids” or testosterone directly. Just keep in mind that with many peptides, you are an early adopter of sorts, and staying informed and cautious is wise. Now, let’s put TRT and peptides side by side to highlight their key differences.
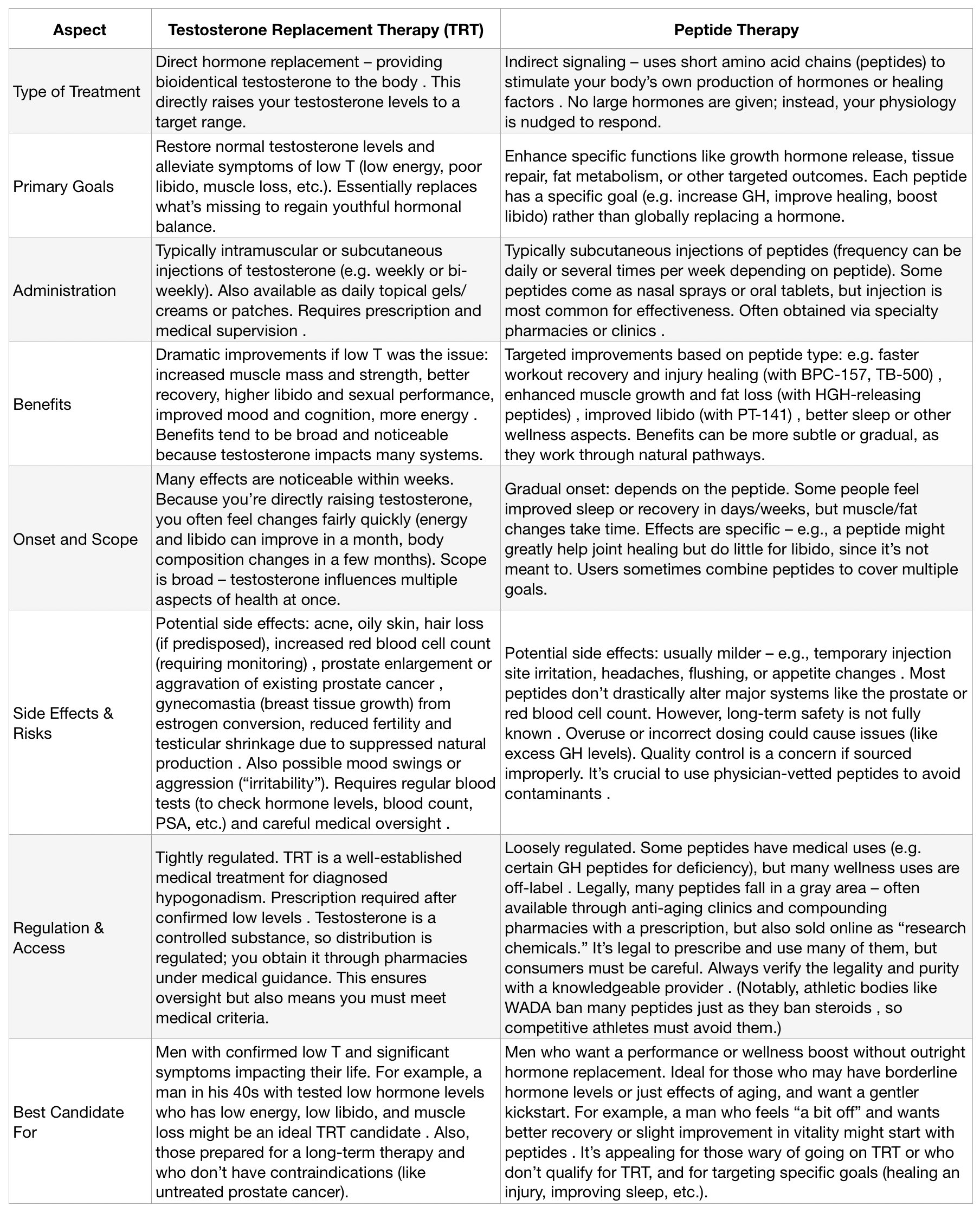
TRT vs Peptides: A Comparison Table
To clarify the distinctions, here’s a quick comparison of TRT and peptide therapy across various factors important to men over 40:
As the table shows, TRT and peptide therapy are quite different in approach. TRT is like replacing an entire engine in a car, whereas peptides are more like fine-tuning the engine you have. One isn’t inherently “better” than the other in all cases – it truly depends on the individual situation. In fact, some advanced treatment plans might use both: for instance, a man on TRT might also use peptides for added growth hormone benefits or injury recovery. However, for most men, it comes down to choosing one path or the other based on their needs and comfort level.
Next, we’ll discuss how to approach that decision and what factors to consider when deciding what’s right for you.
Choosing What’s Right for You: Health Status, Goals, and Next Steps
Given the information above, how should a man over 40 decide between testosterone therapy and peptides (or neither)? The choice should be guided by your health status, your specific goals, and careful consultation with a healthcare professional. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
• Get Lab Work and Evaluate Your Hormone Status: The first step is to understand if you actually have a hormonal deficiency. A simple blood test can measure your testosterone levels (and other hormones like IGF-1, etc.). If your testosterone is unequivocally low for your age – and you have symptoms – TRT might be indicated and could offer the most direct relief . On the other hand, if your T levels are borderline or normal, blasting them higher with TRT might not be appropriate. In such cases, exploring peptides or lifestyle changes to optimize your health could be preferable. Comprehensive lab work can also check growth hormone markers, thyroid, vitamin levels, etc., to see if something else is contributing to your symptoms.
• Define Your Primary Goals: What are you hoping to achieve? Is your libido and sexual function your biggest concern? Are you mostly interested in muscle gains and athletic performance, or is it about overall wellness and aging gracefully? Your goals can point you in one direction or the other. For example, if erectile dysfunction and low libido are plaguing you and you have low T, TRT could significantly help those areas in one sweep. If instead you’re in decent health but want to recover faster from tough workouts and nagging injuries, a peptide like BPC-157 or a growth hormone secretagogue might address that specific need better. TRT is a more general “reset” of male hormones, while peptides let you pick and choose areas to improve. Identify what matters most to you.
• Consider Your Health Profile and Medical History: Your personal and family health history plays a role. If you have a history of prostate cancer or you’re at high risk for it, your doctor will likely steer you away from TRT, or at least proceed very cautiously (since testosterone can feed prostate cancer) . In such a scenario, peptide therapy (which doesn’t directly raise testosterone) might be considered a safer avenue for improving well-being. Conversely, if you have uncontrolled diabetes or severe obesity, growth hormone peptides might not be recommended due to effects on blood sugar, and addressing those conditions first is key. Autoimmune or other conditions could also influence what’s safer or more effective for you. In all cases, a frank discussion with a healthcare provider about your medical history is important to flag any red flags for TRT or peptide use.
• Think About Commitment and Lifestyle: Are you prepared to self-inject regularly or apply medications, and to follow up with doctors? TRT often means a lifelong commitment to maintaining hormone therapy. Stopping can bring back symptoms, so it’s a long-term change in how you manage your health. Peptide regimens might be shorter-term or cyclical, but they can involve multiple injections and possibly trying different peptides to find what works. If you dislike needles or the idea of being on “therapy,” consider that in your decision. Some men are very diligent and don’t mind a routine; others might prefer something with less maintenance. Also, consider lifestyle factors: Are you willing to also exercise and eat right? (Both therapies work best in conjunction with healthy lifestyle, not as standalone magic bullets).
• Safety Comfort Level: Some men feel more comfortable with the well-trodden path of TRT under an MD’s supervision, whereas others feel uneasy about hormones and prefer the notion of peptides because it “feels more natural.” These comfort levels are personal and valid. Peptides may be your best bet if you’re seeking an overall rejuvenation boost without drastically altering one hormone . But targeted testosterone replacement can be transformative if genuinely low testosterone is at the root of your problems . It’s not just about what’s physically safe, but what you psychologically feel good about doing. Just ensure your comfort is backed by facts and medical advice, not Internet hype.
• Natural Alternatives First: Before leaping into any therapy, don’t forget the power of natural lifestyle changes – they are often the first recommended step by doctors for borderline cases . There are natural ways to increase testosterone or improve your vitality that everyone should implement, whether or not you go on TRT or peptides. These include: regular exercise (especially weight training and high-intensity interval training), which can boost testosterone levels ; losing excess weight (fat, especially visceral fat, can lower testosterone) ; improving your diet with adequate protein, healthy fats, and plenty of micronutrients (zinc, vitamin D, etc.) that support hormone production ; getting enough quality sleep, since poor sleep dramatically lowers testosterone and impairs recovery; managing stress, as chronic stress and high cortisol can suppress testosterone; and avoiding overuse of alcohol or opioids which can also lower T . These lifestyle modifications can significantly improve your hormone levels and how you feel – in some cases, men find they no longer need medical therapy because their symptoms resolve with these changes. Even if you do pursue TRT or peptides, a healthy lifestyle will maximize benefits and minimize risks. Think of it as the foundation upon which these therapies build.
• Consult a Knowledgeable Professional: Ultimately, deciding between TRT and peptide therapy isn’t something you should do on your own after reading forums or listening to gym bros. Consulting with a qualified medical professional – ideally an endocrinologist or a men’s health specialist who is familiar with hormone therapies and peptides – is crucial. They can interpret your lab results in context, explain the pros and cons as they specifically relate to you, and help craft a plan. In some cases, the best approach might be a combination: for example, maybe your doctor finds you have low-normal T and not enough to warrant TRT, but you could benefit from peptides plus lifestyle changes, and then re-evaluate. Or perhaps they start you on TRT and later add a peptide for joint health. There are nuances that an expert can navigate. Both TRT and peptide therapy require monitoring (blood tests for TRT; symptom tracking and possibly some labs for peptide effects too). As one clinic put it, healthcare professionals stress that consultation is crucial to safely integrate peptide therapy into a regimen and maximize benefits – the same goes for TRT. So, talk to a doctor who keeps up with the latest in men’s health and can give impartial advice.
Remember, there is no one-size-fits-all solution here . Every man’s body and goals are different. Some men in their 40s might feel fantastic with just a few tweaks in their workout and sleep schedule, never touching any therapy. Another might have legitimately low hormones and truly need TRT to function well. Another might prefer to experiment with legal peptide treatments to see if they can get an edge without committing to testosterone shots. What’s important is making an informed decision with professional guidance, rather than jumping on the latest trend blindly.
Conclusion: Why Education and Guidance Matter
In the debate of TRT vs. peptides, it’s not about declaring a universal winner – it’s about finding what aligns best with your health status and goals. As one wellness magazine aptly stated, choosing between peptide therapy and testosterone “isn’t a matter of good versus bad—it’s about finding what aligns best with your health status, goals, and comfort level.” For men over 40, both paths offer potential benefits, from peptides providing a subtle, supportive nudge to the body’s natural processes to testosterone therapy directly restoring a hormone you might be missing . The key is understanding the differences, and approaching either option with eyes wide open.
Education and professional guidance are critical. Whichever route you consider – be it boosting testosterone or trying peptides – do so with thorough research and in consultation with a healthcare provider. An experienced doctor can help ensure you have realistic expectations and that your plan is safe. As experts emphasise, none of these interventions outshine the importance of a balanced lifestyle and a foundation of healthy habits . They are tools that, when used appropriately, can enhance your quality of life. But they are not magic shortcuts to eternal youth, and they come with responsibilities.
Finally, keep your long-term well-being front and center. The goal of any therapy should be to help you feel stronger, more vital, and healthier for the long haul – not just to chase a short-term boost . Avoid the temptation of black-market solutions or unsupervised regimens; the risks there far outweigh any reward . Instead, take a thoughtful, measured approach. Ask questions, weigh the answers, and consider starting with the least invasive options. If you do proceed with TRT or peptides, monitor your body’s response and keep communication open with your doctor.
Bottom line: For men over 40 seeking to maintain or regain their edge, TRT and peptide therapy are both viable avenues, each with pros and cons. With the right knowledge and medical guidance, you can make an informed decision on which path, if any, is right for you. And if you’re still not sure, you don’t have to navigate it alone – consider scheduling a consultation with a men’s health specialist who can help chart out a personalised plan. The journey to better performance and health is highly individual, but armed with education and the support of professionals, you’ll be well on your way to making the best choice for your future.
*(Note: This article is for educational purposes and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a licensed healthcare provider before starting or changing any treatment.)